What to know about salivary gland infections
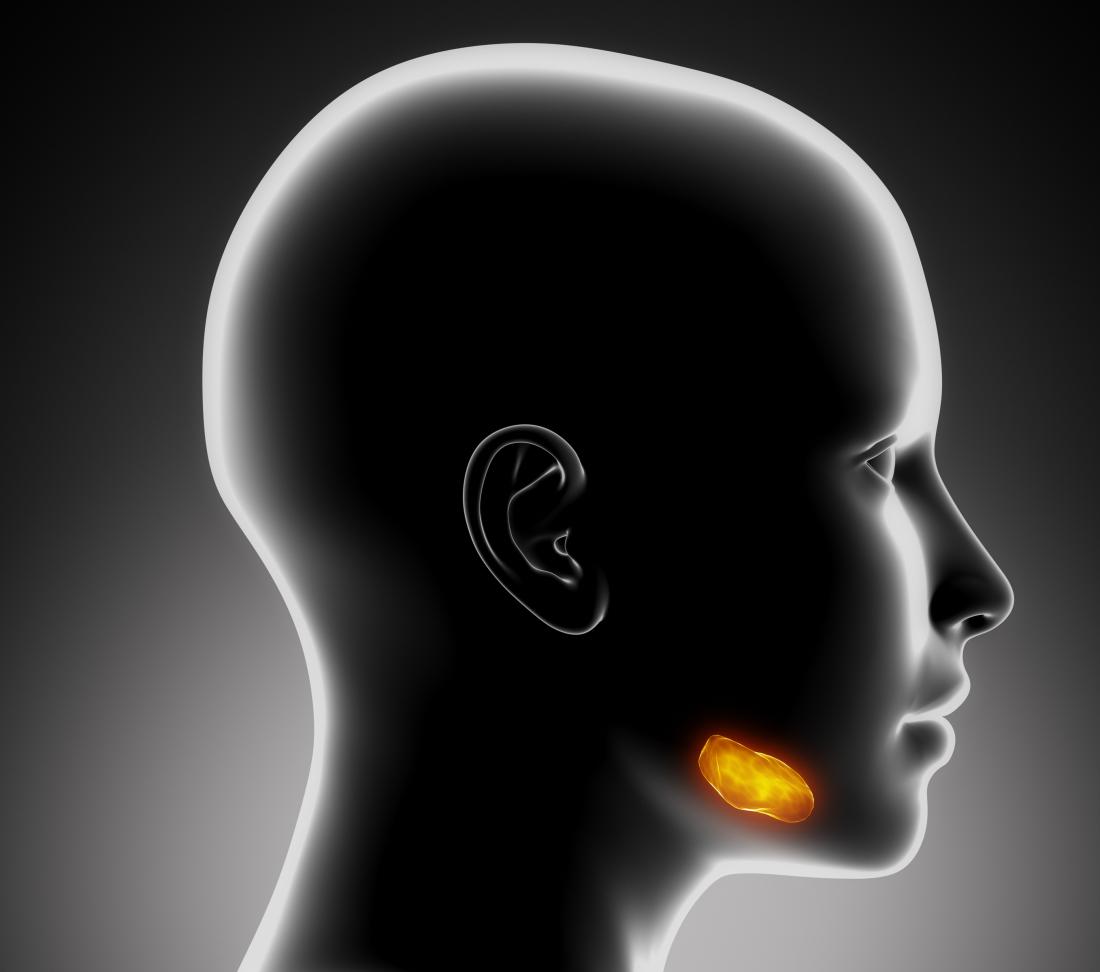
People get salivary gland infections when bacteria or viruses get into the salivary glands, which are a group of glands in the head and neck.
Salivary gland infections most commonly develop in the two main glands, which are located in the front of the ear (the parotid gland) and under the chin (the submandibular gland).
A salivary gland infection, also called sialadenitis, can cause a blockage in the saliva ducts due to inflammation. This can lead to pain, tenderness, and swelling.
In this article, we discuss the types, causes, and treatments of salivary gland infections.
Causes of salivary gland infections
A salivary gland infection occurs when bacteria or viruses infect a gland that produces saliva.
People can get a salivary gland infection from having:
- a reduced flow of saliva due to medical conditions, such as dry mouth
- poor oral hygiene which increases the growth of bacteria, such as Staphylococcus aureus or Haemophilis influenzae
- a blockage in their salivary glands from a tumor, abscess, or salivary gland stone
- severe dehydration, which may be due to illness or surgery
Blockages in the salivary glands can cause inflammation, making the glands more vulnerable to infection.
Also, inflamed salivary glands tend to produce less saliva, which flows more slowly than usual. As a result of this, the saliva sometimes pools in the glands, allowing the concentration of bacteria or viruses within the saliva to increase.
Some of the more common causes of salivary gland obstructions include:
- salivary gland stones
- kinks in the salivary ducts
- tumors
- abnormally formed salivary glands
Bacteria tend to cause more salivary gland infections than viruses do. But some of the more common viruses known to cause of salivary gland infections include:
- HIV
- mumps
- parainfluenza types 1 and 2
- influenza A
- herpes
- coxsackievirus