Philippine students suffer in wilting heat, thwarting education efforts

Sweltering heat in the Philippines can curb farm production, disrupt water and power, and weigh on businesses. It also affects students, hampering the Southeast Asian nation's efforts to catch up to its neighbors in education.
Heat indices have hit 50 degrees Celsius in various regions in the Philippines, as the weather phenomenon El Nino intensifies the heat enveloping the nation in its summer months of March to May.
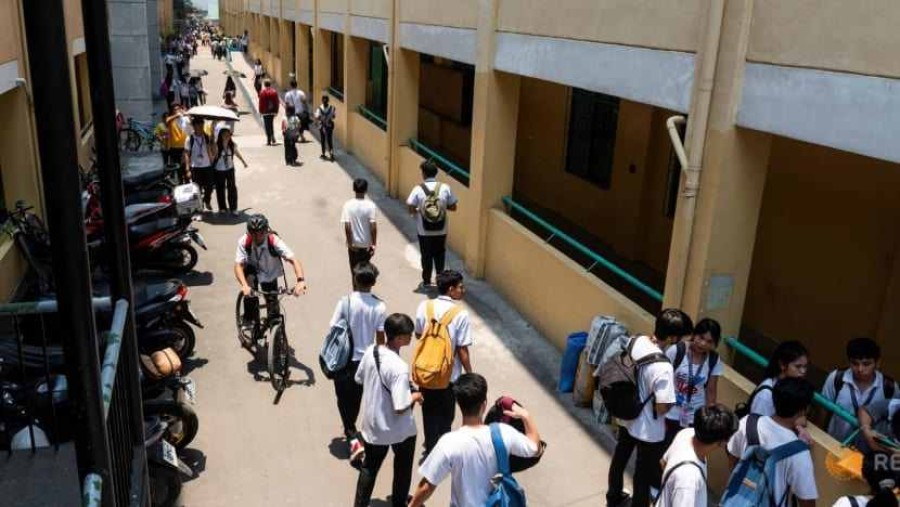
Thousands of schools have suspended classes due to the heat, affecting more than 3.6 million students, education ministry data shows.
"We're expecting more class suspensions in May because of the heatwaves. We're seeing an average of more than 52 degrees Celsius, so you could imagine how stressful that would be for learners," said Xerxes Castro, basic education adviser for Save the Children Philippines.
The wilting heat - part of a band spreading across much of South and Southeast Asia, exacerbated by climate change - makes learning harder for students.
Children are particularly vulnerable to heat-related illnesses such as dizziness, vomiting and fainting when exposed to extreme heat for long periods, according to Save the Children Philippines.
Students and teachers have expressed concerns about difficulties in remote teaching and learning, especially in poorer areas where homes are not conducive for studying and may lack access to good internet connectivity.
"I could not focus because I get dizzy" from the heat, Esmaira Solaiman, a 20-year-old senior high school student whose learning was delayed during the pandemic, said after attending an online class from home.
Students attending in-person classes in the capital Manila resort to portable fans, notebooks and even cardboard boxes for a bit of breeze to offer relief.
"My blood pressure is already increasing because of the heat," said 62-year-old secondary school teacher Memia Santos. "Our backs are wet and at times we get dizzy."